DIAMOND EDUCATION
Diamond education is the understanding of the four "C"s" of diamonds: colour, cut, carat, and clarity, which are the essential elements to consider when purchasing a diamond and impact diamond quality and pricing.
What is Diamond?
A diamond, a crystalline celestial whisper, is nature's alluring masterpiece crafted deep within the Earth's embrace. Born from the sacred marriage of time, pressure, and carbon, it emerges as a radiant embodiment of cosmic secrets and geological wonders.
4CS Introduction
At Bodra Brothers, we believe that learning about diamonds is essential to choosing your ideal stone. The International Grading System and the 4Cs were developed by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). Colour, clarity, cut, and carat weight are the four Cs. Each diamond attribute has a significant role in determining the overall diamond quality.
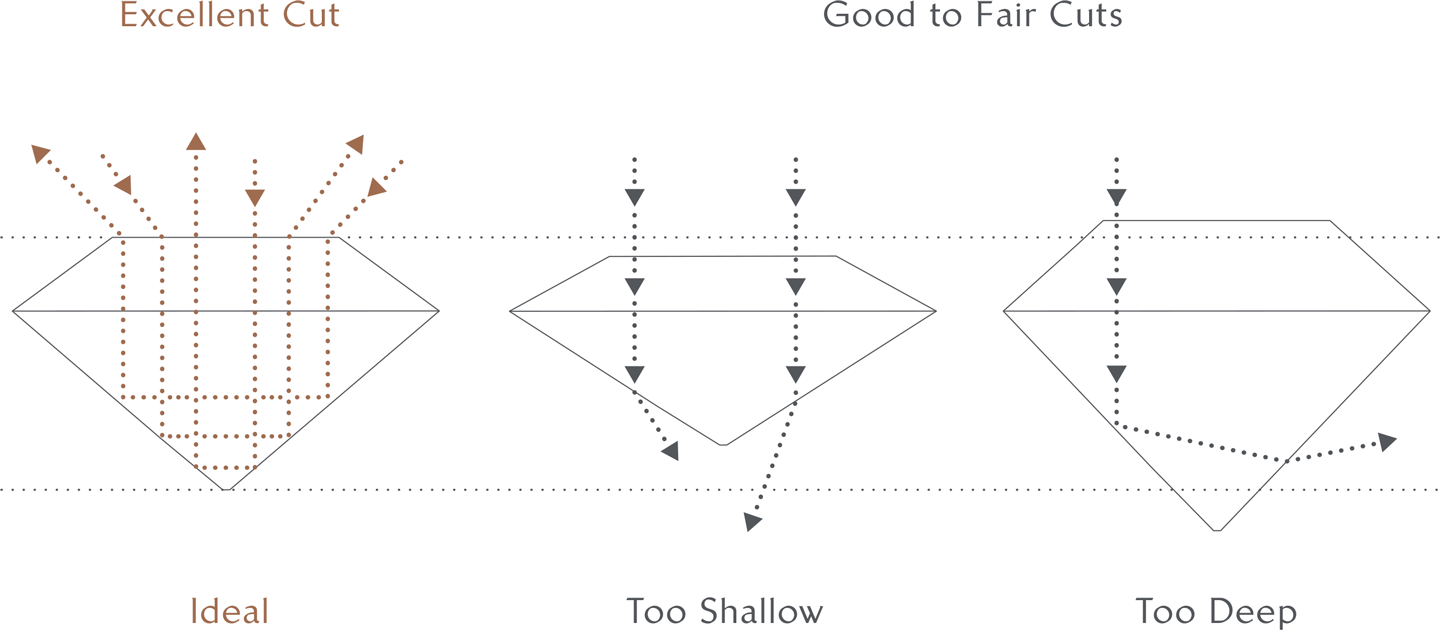
Cut
The cut of a diamond greatly influences its brightness. An appropriately cut diamond with exactly symmetrical and aligned facets will reflect light superbly, resulting in unequalled brilliance. True expertise is required to create facets with ideal proportions that maximize light and intensify a diamond's distinctive shine.
The overall proportions of a diamond as well as the size and placement of its many reflective surfaces or facets, all play a role in "cut." The uniformity and balance of these factors can significantly impact how the stone collects light and reflects it back to the eye.
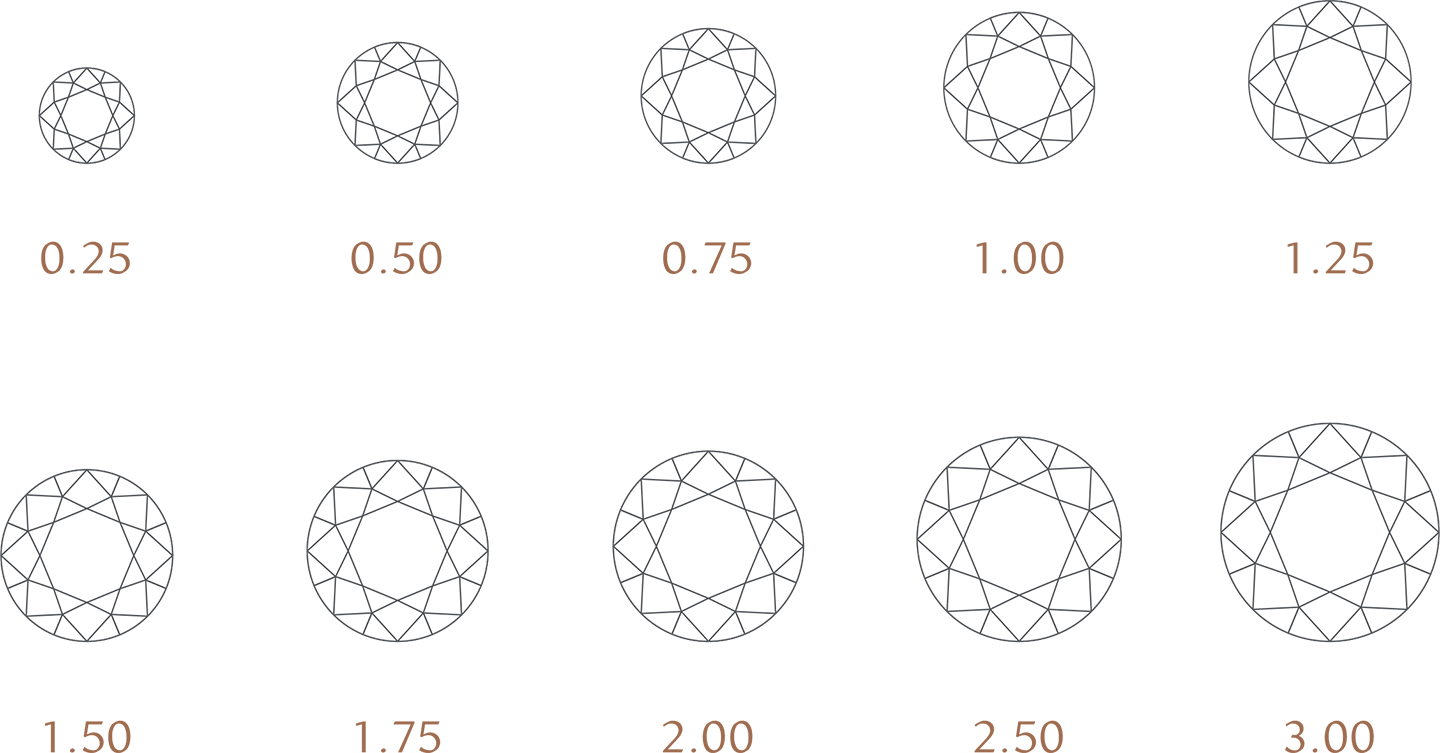
Carat
Carats, not to be confused with gold karats, are the weight of a diamond. Each carat is made up of 100 points. A point equals one-fifth of a gramme, so one carat is approximately two grammes.
Because larger diamonds are uncommon, the higher the carat weight, the higher the value. Diamonds with the same carat weight may not have the same value since they behave differently regarding other desirable features.
Clarity
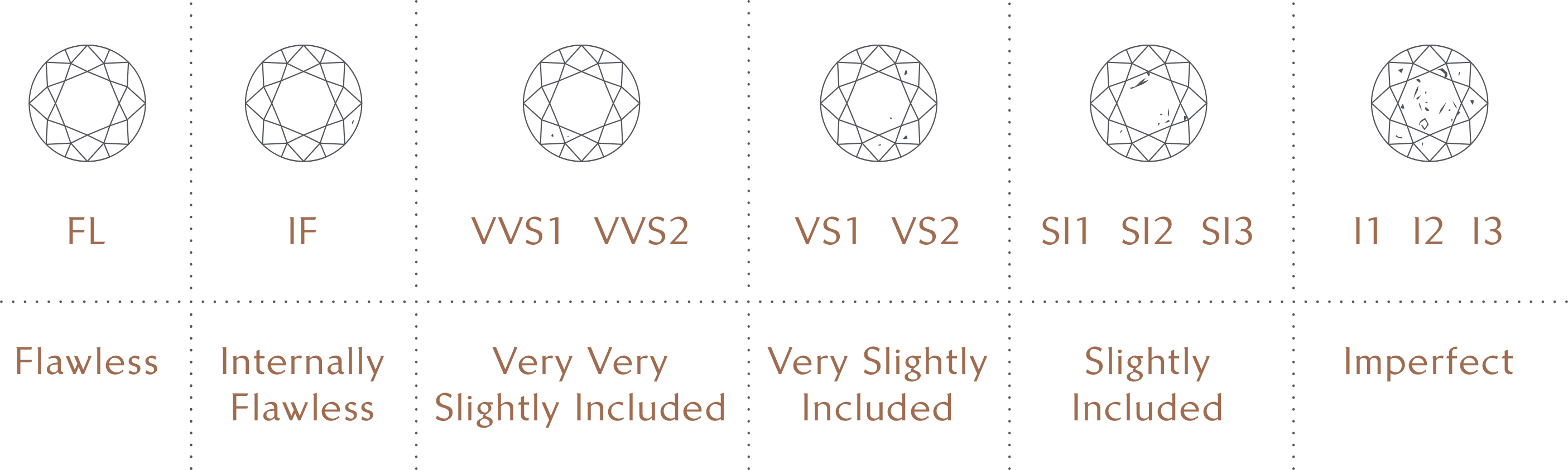
Many diamonds look perfect to the naked eye, but looking at them under 10x magnification, you can see flaws like clouds, feathers, and tiny crystals. One of the main things determining a diamond's worth is its appearance. This makes it hard to find the rarest diamonds.
Flawless (FL) and Internally Flawless (IF) diamonds are the rarest clarity levels, and a qualified gemologist must grade them to ensure they are correct. Even if you can't tell the difference, these small changes can greatly affect how rare something is and, in turn, how much it's worth. The international method of grades is shown in the chart below.
Colour
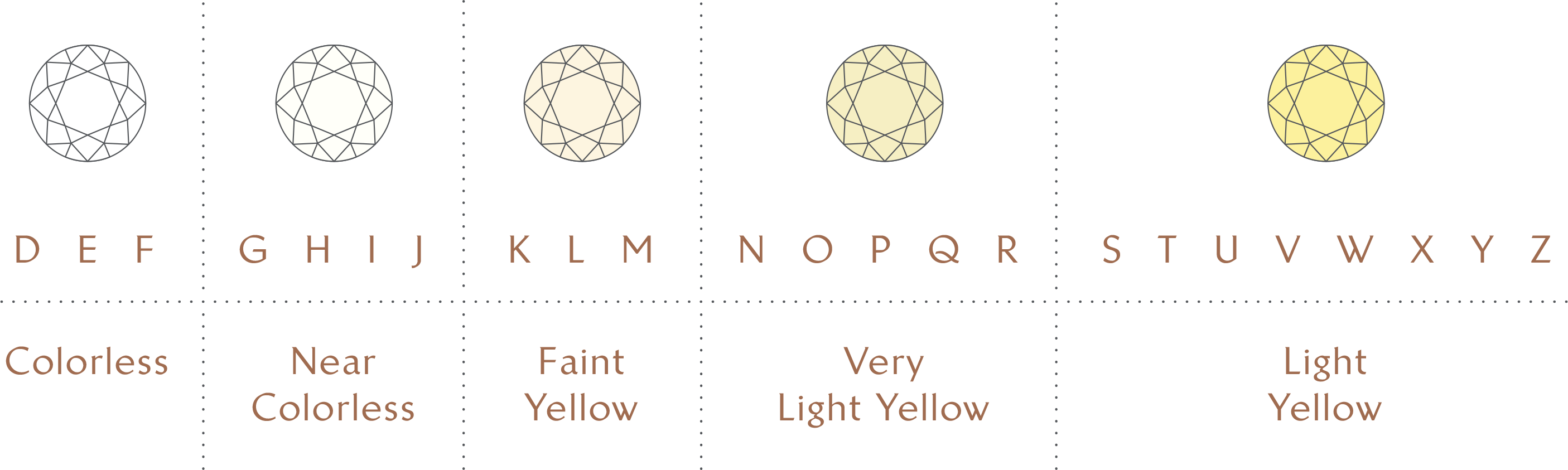
Except for some fancy-coloured diamonds, the most valuable diamonds are those with the least colour. Transparent diamonds can range in colour from colourless (D-F), nearly colourless (G-J), mild yellow (K-L), to light yellow (Z). Diamonds with no colour at all are incredibly unusual.
Rare and exquisite hues can develop in diamonds when traces of other minerals are present. Blue, dazzling yellow, red, brown, pale green, pink, and violet are among the "fancy" colours. Coloured diamonds are extremely rare, which makes them highly sought-after and potentially quite valuable.